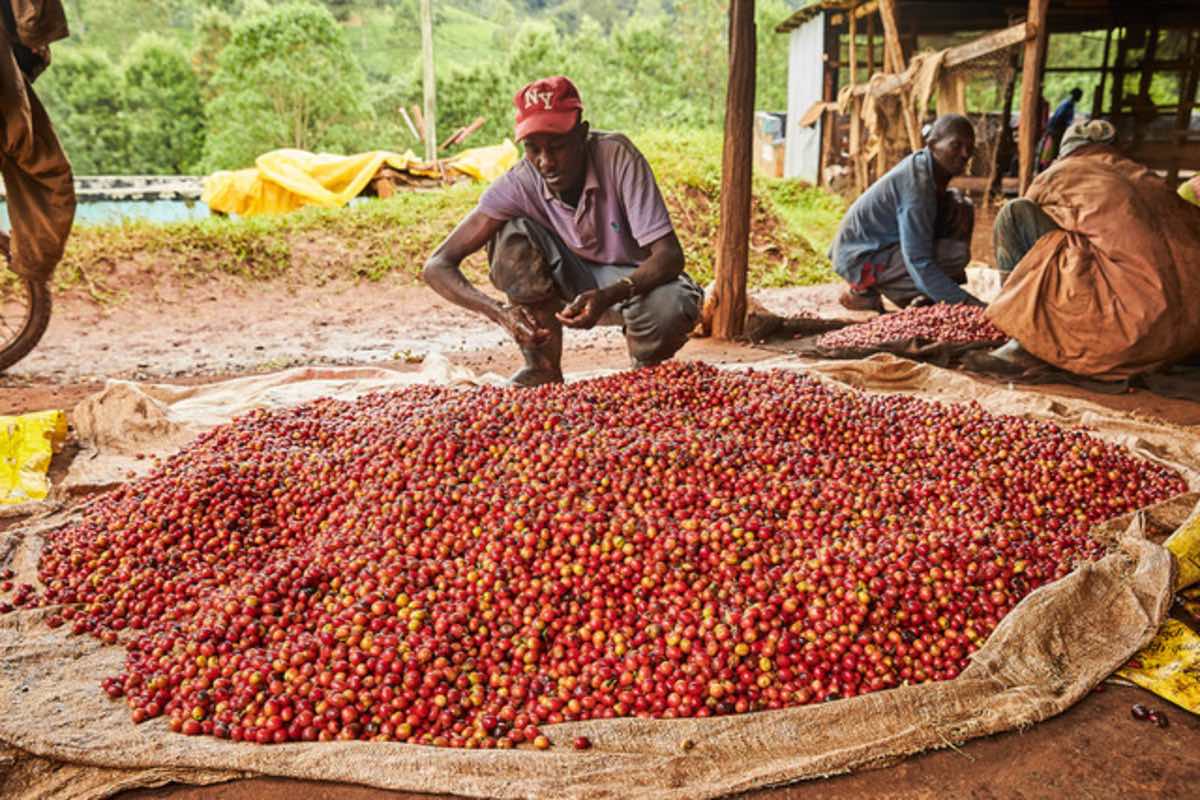
Battling Common Coffee Farming Challenges
Introduction: Battling Common Coffee Farming Challenges: Pests and Diseases in Kenya
Coffee is not just a beverage; it’s a lifeline for economies and livelihoods across Kenya. Yet, the journey from bean to cup is fraught with challenges, with pests and diseases being some of the most menacing adversaries. In this article, we will shed light on the top common diseases and pests in coffee farming in Kenya and discuss effective mitigation strategies for farmers to safeguard their crops and ensure bountiful harvests.
1. Coffee Berry Disease
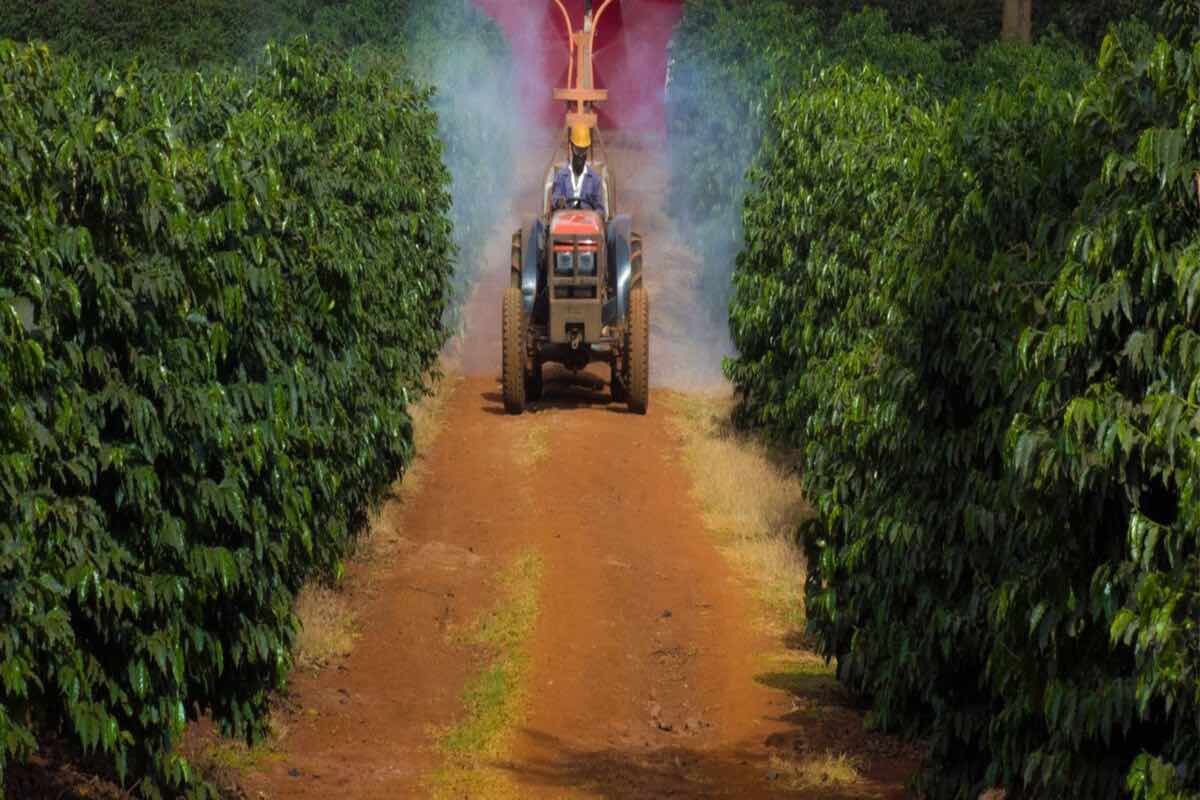
The Coffee Berry Disease (CBD), caused by the fungus Colletotrichum kahawae, has been a perpetual headache for coffee farmers in Kenya. CBD attacks the coffee berries, causing them to wither, turn brown, and drop prematurely. Combatting CBD demands proactive measures such as planting disease-resistant coffee varieties, maintaining proper spacing between coffee trees for adequate air circulation, and timely removal and destruction of infected berries.
2. Coffee Leaf Rust
Coffee Leaf Rust (CLR), caused by the fungus Hemileia vastatrix, is another notorious enemy. Its telltale signs include orange powdery spores on the undersides of leaves, leading to defoliation and reduced photosynthesis. To thwart CLR, farmers should adhere to strict pruning practices that ensure proper sunlight penetration and air circulation. Fungicides and copper-based sprays can also aid in controlling its spread.
3. Antestia Bugs
Antestia bugs, known as “stink bugs,” pose a dual threat by both feeding on coffee cherries and transmitting the Coffee Withering Bacteria (CWB) responsible for coffee wilt disease. Early detection is key, and farmers should implement traps and regular monitoring to keep these pests in check. Integrated pest management strategies, such as introducing natural predators, can contribute to effective antestia bug control.
4. Root-Knot Nematodes
Root-knot nematodes are microscopic yet mighty adversaries, attacking coffee plant roots and causing stunted growth, wilting, and reduced yields. Crop rotation, using resistant rootstocks, and implementing soil solarization techniques can help mitigate nematode infestations. Ensuring proper drainage and using organic matter-rich soil can also discourage nematode proliferation.
5. Aphids
Aphids, tiny insects that suck sap from coffee leaves, can weaken the plant’s vigor and transmit viruses. Employing natural predators like ladybugs and lacewings can be an eco-friendly way to control aphid populations. Pruning affected plant parts and avoiding excessive nitrogen fertilization can also curb aphid infestations.
Conclusion
While the challenges of pests and diseases are formidable, the resilience of Kenya’s coffee farmers is equally remarkable. Combating these threats requires a combination of vigilance, knowledge, and proactive strategies. By implementing disease-resistant coffee varieties, practicing good agricultural hygiene, utilizing integrated pest management techniques, and fostering a culture of continuous learning, coffee farmers can safeguard their crops and ensure thriving harvests. The battle against pests and diseases may be ongoing, but with the right tools and tactics, Kenya’s coffee industry can continue to thrive and prosper.