Kenya Coffee Production and Regulatory Changes
Introduction : Statistical Report on Kenya Coffee Production and Regulatory Changes
Sources: Nairobi Coffee Exchange, Capital Markets Authority, Coffee Research Institute, and FAS Report
1. Overview of Kenya Coffee Production in 2023:
In 2023, Kenya’s coffee industry has experienced a remarkable resurgence, witnessing a significant rebound in coffee production. This growth can be attributed to a combination of factors, including favorable weather conditions, increased adoption of modern agricultural practices, and government initiatives aimed at boosting the coffee sector.
2. Kenya Coffee Production Data:
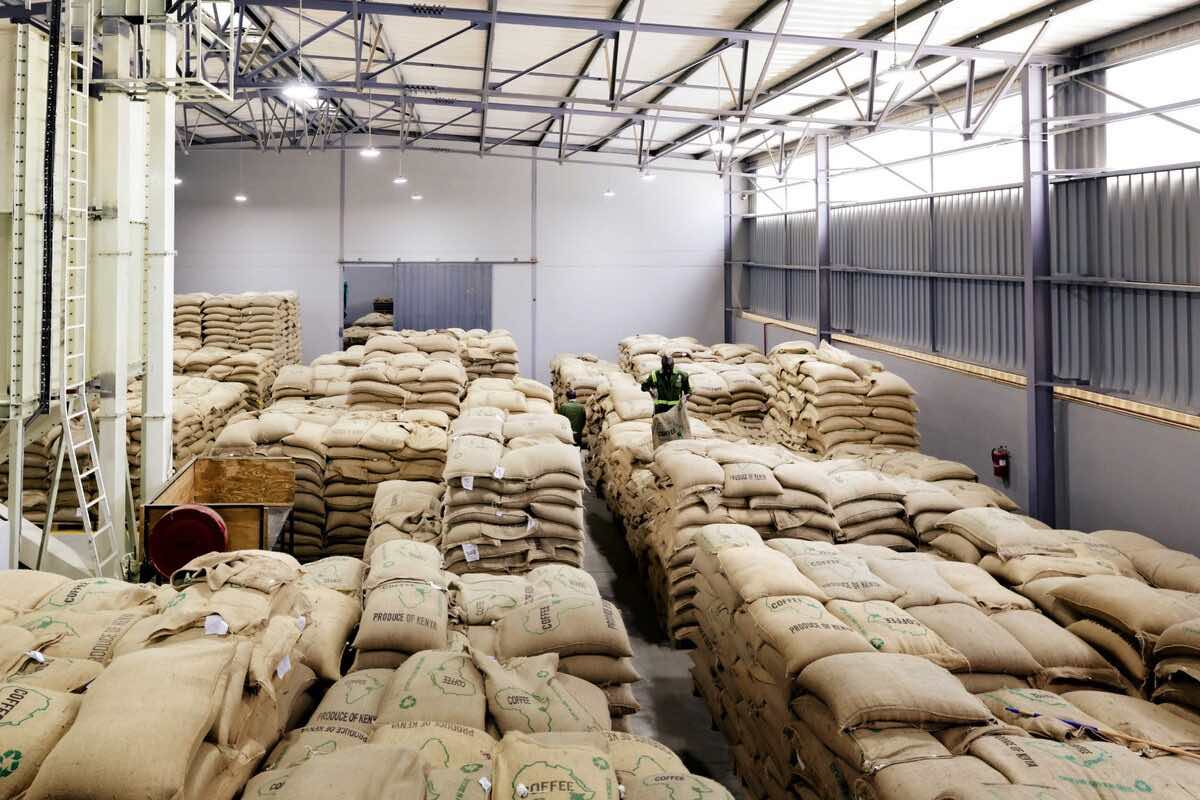
– Kenya’s marketing year (MY) 2023/24 coffee production is forecast to increase 6.7 percent to 800,000 bags due to a recovery from drought conditions and higher fertilizer application.
Area harvested is expected to remain flat at 105,000 hectares, as new plantings are curtailed due to a shortage of planting materials and as losses associated with conversion of coffee plantations to real estate slows. MY 2023/24 coffee exports are anticipated to grow 5.5 percent to 760,000 bags as higher production increases exportable supplies.
3. Coffee Varieties and Regions of Production:
– Arabica Coffee: Predominantly grown in regions with higher altitudes, such as Nyeri, Kirinyaga, Embu, and Meru.
– Robusta Coffee: Cultivated in lowland areas, including Kisii, Bungoma, and Kakamega.
4. Impact of Regulatory Changes on Kenya’s Coffee Sector:
The Kenyan government has made significant regulatory changes to enhance the coffee sector’s performance and sustainability. These changes have focused on improving transparency, market access, and ensuring fair pricing for coffee growers.
5. Regulatory Changes Implemented:
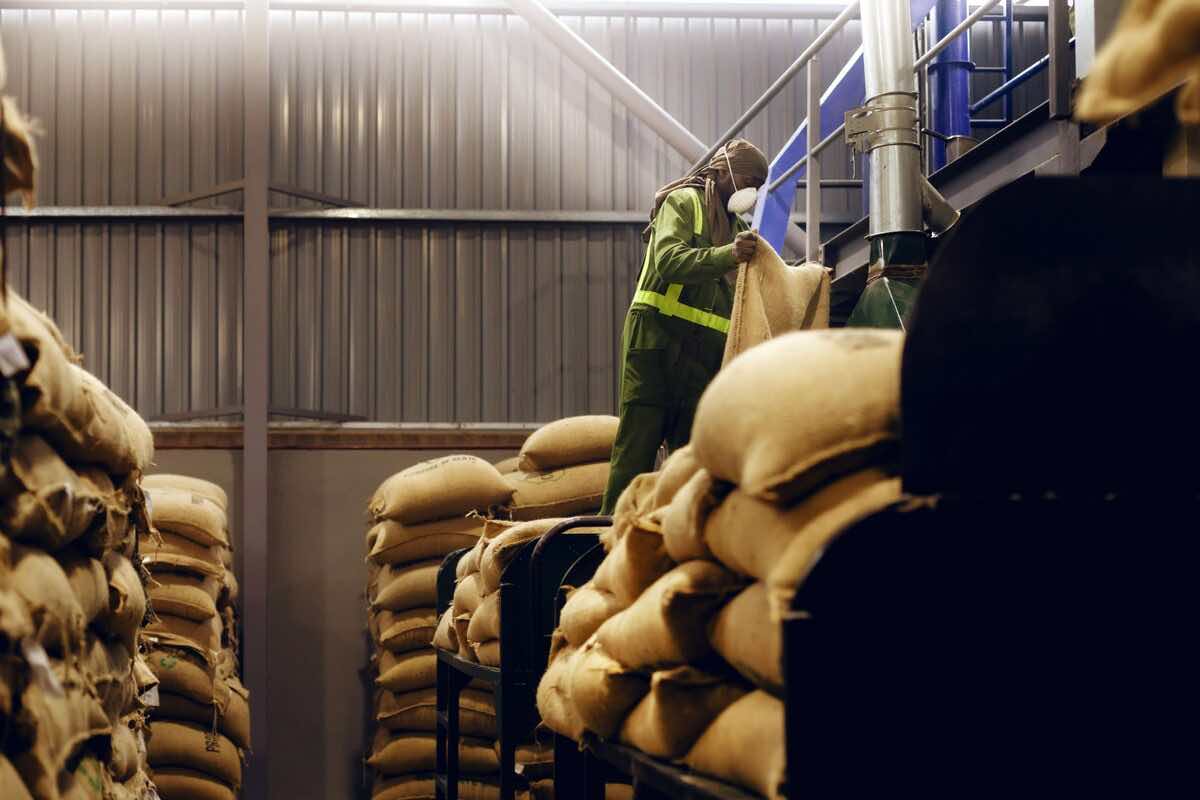
5.1. Nairobi Coffee Exchange Reforms:
– Introduction of Electronic Trading Platform: The Nairobi Coffee Exchange implemented an electronic trading platform, enabling more efficient and transparent coffee trading. This move has reduced transaction costs, minimized middleman involvement, and provided better price discovery for coffee farmers.
– Direct Market Access for Coffee Farmers: Through the electronic trading platform, coffee farmers gained direct access to buyers, allowing them to negotiate prices and sell their produce without intermediaries.
5.2. Capital Markets Authority (CMA) Involvement:
– Securitization of Coffee Crop: The Capital Markets Authority, in collaboration with the coffee industry stakeholders, introduced innovative securitization measures. These measures allowed coffee farmers to use their future crop as collateral for loans, enabling them to invest in modern agricultural technologies and better farm practices.
5.3. Coffee Research Institute Initiatives:
– Sustainable Farming Practices Promotion: The Coffee Research Institute (CFI) intensified its efforts to promote sustainable farming practices, such as shade-grown coffee cultivation and eco-friendly pest management techniques. These practices have contributed to improved coffee quality and environmental conservation.
– Climate-Resilient Coffee Varieties: The institute developed and disseminated climate-resilient coffee varieties, aiding farmers in adapting to changing weather patterns and mitigating the impact of climate change on coffee plantations.
5.4. FAS Report:
– Market Analysis and Forecast: The Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) report highlighted the increasing global demand for high-quality Kenyan coffee. The report projected a substantial rise in coffee exports, creating new market opportunities for Kenya’s coffee industry.
6. Impact of Regulatory Changes on Kenya Coffee Sector:
– Increased Coffee Production: The regulatory changes have incentivized farmers to invest in their coffee plantations, leading to a substantial increase in coffee production.
– Enhanced Quality: The adoption of sustainable farming practices and improved post-harvest handling has resulted in better-quality coffee beans, fetching premium prices in international markets.
– Empowerment of Coffee Farmers: The regulatory changes have empowered coffee farmers by providing them with direct access to buyers and fairer pricing, improving their income and livelihoods.
7. Future Outlook:
Kenya’s coffee industry is poised for continued growth, driven by the positive impact of regulatory changes, increased investment in modern agricultural practices, and rising global demand for premium coffee. The government’s commitment to the coffee sector’s development, coupled with continuous support from various institutions, promises a bright future for Kenya’s coffee farmers and exporters.
**Note:**
The data and information presented in this report are based on available statistics and reports from reputable sources. However, it is essential to cross-reference with the latest data and updates for the most accurate and up-to-date information.